Table of Contents
Introduction – 5 Ancient and Earliest Civilizations of the World
5 Ancient and Earliest Civilizations of the World. In this article, we will try to briefly about the civilization of Mesopotamia, Indus Valley civilization, Ancient Egyptian civilization, Ancient Chinese civilization, and Ancient Greece. These 5 civilizations were the first ones to flourish in the History of Mankind.
The Civilization of Mesopotamia (3500 BCE – 2334 BCE)
One of the first and most significant civilizations in the history of the world originated in Mesopotamia, an area located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Mesopotamia, which is considered the beginning of civilization, developed for thousands of years and made a long-lasting mark on human history. The Mesopotamian civilization established the path for future civilizations with its outstanding achievements in architecture, literature, law, and complex society.
The civilization of Mesopotamia contained a larger area and included many civilizations within itself. We can call it a collection of civilizations and it contained, Babylonia, Assyria, Sumer, Akkad, and others. Babylonia was one of the Kingdoms within the Mesopotamian Civilization.
The empire of Babylonia existed from 2100 to 1100 B.C. While the Assyrian Empire exited from 1100 to 600 B.C. The other one, Mardin Empire existed between 600-539 B.C.
The Sumerians who were neither Semitic nor Aryan in racial origin had developed a high degree of civilization by 3,500 B.C., in Sumeria (modern Iraq). They knew the art of writing and they opened libraries with clay books.
In 2,700 B. C., Semitic Akkadians conquered Sumeria. At that time the Amorites, another Semitic tribe, were ruling the city of Babylonia. About 1300 B. C., another Semitic people, who were living in Assur, became very strong and conquered Babylon.
In 732 B. C., the Assyrians captured Damascus (modern Syria). The conquest of Egypt, Palestine, and adjoining countries followed soon.
The Assyrian empire collapsed in 612 B.C. when the Chaldeans helped by the Medes and the Persians captured Nineveh. It was King Nebuchadnezzar (604-561 B. C.),-the ruler of the Assyrian people, who constructed the famous hanging gardens of Babylon to please his wife. Nineveh fell to the Persians in 538 B. C.

Do you know? Mesopotamia gave the world’s first legal laws, which is known as the Code of Hammurabi. This code was established by King Hammurabi of Babylon in the 18th century BCE. This code defined laws and regulations controlling all elements of life. It mirrored the notion of “an eye for an eye” and established principles for justice, property rights, and social order.
Mesopotamians made important progress in multiple fields of science. They developed a complex mathematical system, including a base-60 number system, which we use even today as we split hours into 60 minutes and circles into 360 degrees. They also performed astronomical observations, wrote about celestial body movements, and created calendars.
You can get an understanding of their knowledge of art and architecture as they built the Hanging Garden of Babylonia.

This is Hammurabi’s stone with the legal code written on it. This was the first legal code in world’s history. At the top of the stone, it is Hammurabi with Babylonian god of justice. This code of law is based on “An Eye For An Eye”.
Do you think it is still followed in some countries? Please comment.
As this post is a brief description, you can read more on The Code of Hammurabi and explore how it is an eye from an eye.
Indus Valley Civilization (3300 BCE – 1300 BCE)
India was enjoying an advanced and the best-organized civilization among her contemporaries. Arms and utensils of stone, copper, and bronze were extensively in use. The use of cotton for textiles was already known.
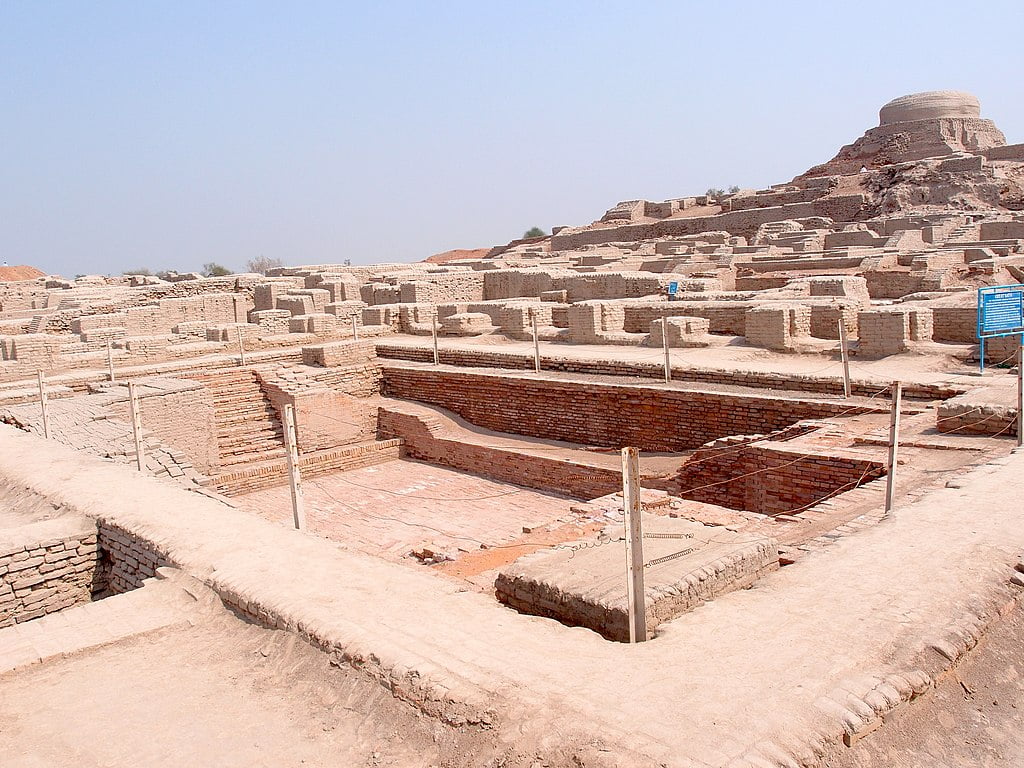

The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, is one of human history’s most interesting and enigmatical ancient civilizations. From roughly 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, this extraordinary civilization lived in what is now modern-day Pakistan and parts of northwest India in the Indus River region. Despite its major contributions to ancient history, much of the Indus Valley Civilization remains a mystery.

The towns of the Indus Valley Civilization were carefully planned and had advanced urban infrastructure. Cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa had well-organized layouts with street lines, brick-built houses, public baths, and an efficient drainage system that showed their technical expertise. The cities were well-planned, pointing out the civilization’s focus on public health and cleanliness.
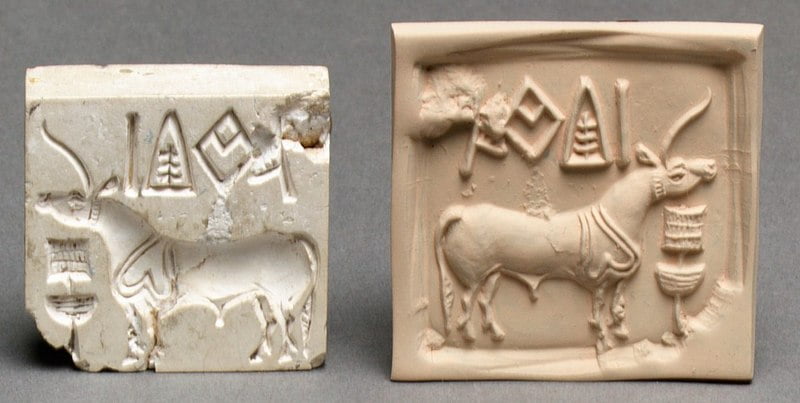
Indus Valley had trade relations with Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), Iran, and Afghanistan. The archeological discoveries of clay seals and other objects point out that the people of the Indus Valley used to trade in precious metals, jewels, textiles, and agricultural products. The trade was well-developed and it was a major contributor to civilization’s economic success. Moreover, it helped in cultural interactions with other civilizations.
The Indus script, a one-of-a-kind writing system, has remained unsolved to this day. The civilization’s seals and inscriptions give insights into their written communication, but the script’s meaning is unknown. The script’s intricacy, along with the lack of a multilingual Rosetta Stone-like artifact, has made decipherment difficult. Uncovering the secrets of the Indus script might help us understand their language, culture, and history.
The agricultural activities of the civilization were supported by the rich and fertile lands of the Indus River basin. The people of the Indus Valley civilization grew crops such as wheat, barley, rice, and cotton. They used advanced irrigation systems for agriculture. In archeological exploration, people have found granaries and grain storage facilities which suggest that securing the food was important and there was a surplus production.
The Indus Valley Civilization has a rich artistic history. Stone seals, sculptures, pottery, and jewelry with complex carvings show their artistic abilities and skill. Their artwork’s precision and attention to minute details indicate an improved sense of design. Animal depictions, such as the well-known “Dancing Girl” sculpture, provide insights into their society and cultural beliefs.
While facts regarding the social structure of the Indus Valley Civilization are little, it is believed that they had a well-organized society with various social classes. The presence of public buildings, religious structures, and detailed bath complexes indicates the importance of community areas as well as a possible focus on religion and religious rituals. Due to the poor decipherment of their script, the significance of their religious ideas, deities, and rites remains uncertain.
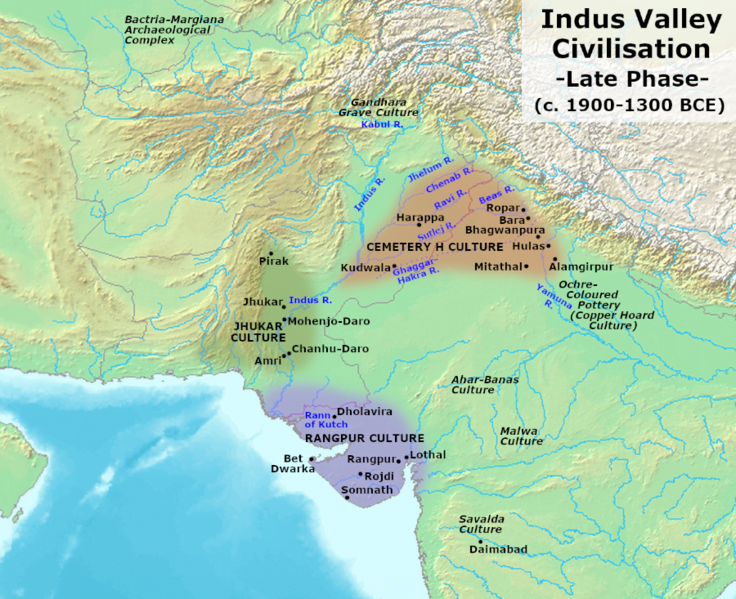
The Indus Valley Civilization is a tribute to past culture’s creativity and achievements. Its well-planned cities, extensive urban infrastructure, efficient trade networks, and innovative thinking indicate the civilization’s excellent level of progress. While many issues remain unresolved, the Indus Valley Civilization’s contributions to human history and enduring effects continue to capture our interest and motivate greater investigation.
Ancient Egyptian Civilization (3100 BCE – 332 BCE)

The earliest Egyptian civilization was flourishing in the Nile valley, some thousands of years before the birth of Christ. It is remarkable that in 4241 B. C., the ancient Egyptians, who were Hamites, invented a yearly calendar of 365 days. A great line of more than 30 Egyptian Pharaohs ruled Egypt one after another till the country was invaded by the Assyrians in the 7th century B. C.
The Persians conquered Egypt in 525 B.C. This thriving land with her ancient record of civilization finally lost her freedom and remained in fetters.
After the death of Cleopatra in 31 B. C., Egypt was conquered by the Romans. The Arabs captured Egypt in 641 A.C., and ever since then, Islam has dominated this land.
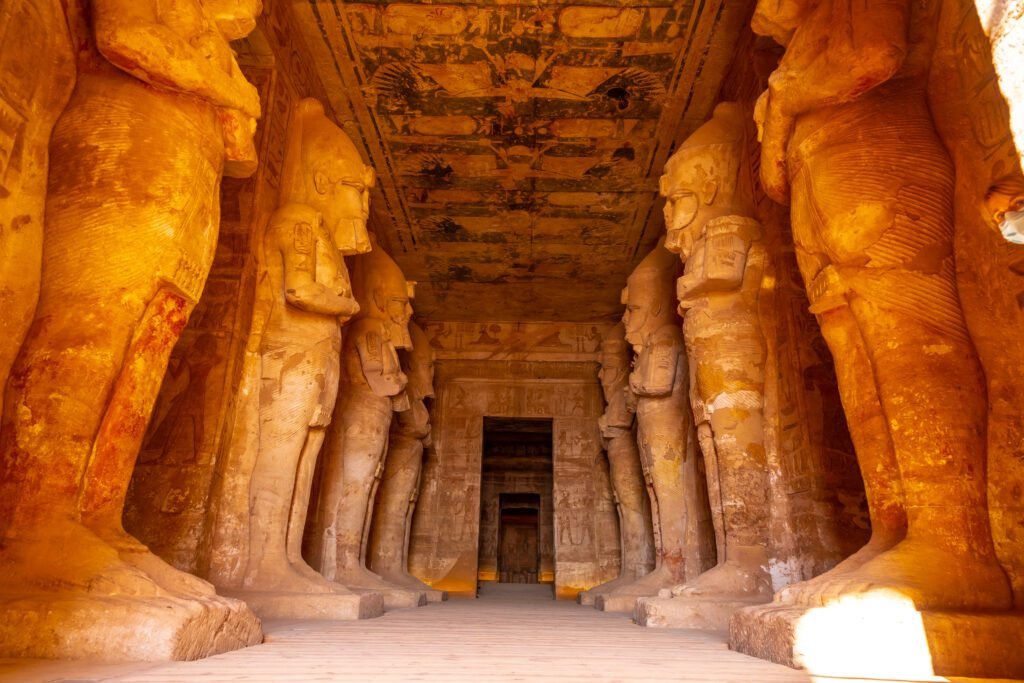
The government of pharaohs considered divine rulers as crucial figures in the civilization’s religious beliefs and was at the center of Ancient Egypt’s social and political structure. Pharaohs were seen to be mediators between the gods and mankind, wielding enormous authority and controlling all elements of Egyptian society, such as religion, government, and justice.
The Great Pyramids of Giza, particularly the renowned Pyramid of Khufu (Cheops), are the highest point of ancient Egyptian architecture and technical wonders. These massive structures were precisely created as spectacular tombs for the pharaohs, featuring elaborate pathways and rooms. The pyramids are a tribute to the Egyptians’ mastery of mathematics, engineering, and the immense willpower necessary to build lasting structures.
The ancient Egyptian variety of gods and goddesses was broad, with each God linked with different elements of life and nature. Egyptians believed in the afterlife, and extensive rites such as mummification and burial were performed to facilitate a smooth transition into the next world. Mythology, as seen in complex murals and stories like the Osiris myth, served as a framework for religious and moral ideals.
Hieroglyphs, a form of symbol-based writing system, were a unique feature of ancient Egyptian society. Hieroglyphs were used by the Egyptians on temple walls, architectural constructions, and scrolls of papyrus. In the nineteenth century, the decoding of the hieroglyphs revealed important insights into the civilization’s history, literature, and daily life.
The ancient Egyptians made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and other areas. They created advanced mummification processes, demonstrating an in-depth understanding of the human body’s structure. The Great Sphinx’s design and alignment with celestial bodies demonstrate their astronomical knowledge. In addition, the use of herbs and natural remedies in medical procedures established a foundation for future developments in medicine.
Egyptian art has attracted scholars and art fans for thousands of years because of its distinctive style and adherence to difficult norms. The Egyptians had expertise in portraying sacred themes, pharaohs, and daily life in wall paintings, sculptures, and beautiful jewelry. Their paintings got depth and meaning because of the development of creative methods like bas-relief and symbolic colors.
The Ancient Egyptian civilization continues to enchant the globe with its awe-inspiring pyramids, stately pharaohs, and rich cultural legacy. Ancient Egypt’s contributions to human civilization are immense, ranging from colossal architectural feats to advances in science, medicine, and art. This magnificent civilization’s legacy lives on via its surviving monuments, preserved relics, and the collective interest it has instilled in generations all across the world. The ancient Egyptians’ quest for an everlasting afterlife, as well as their achievements in this world, earned their place among history’s great civilizations.
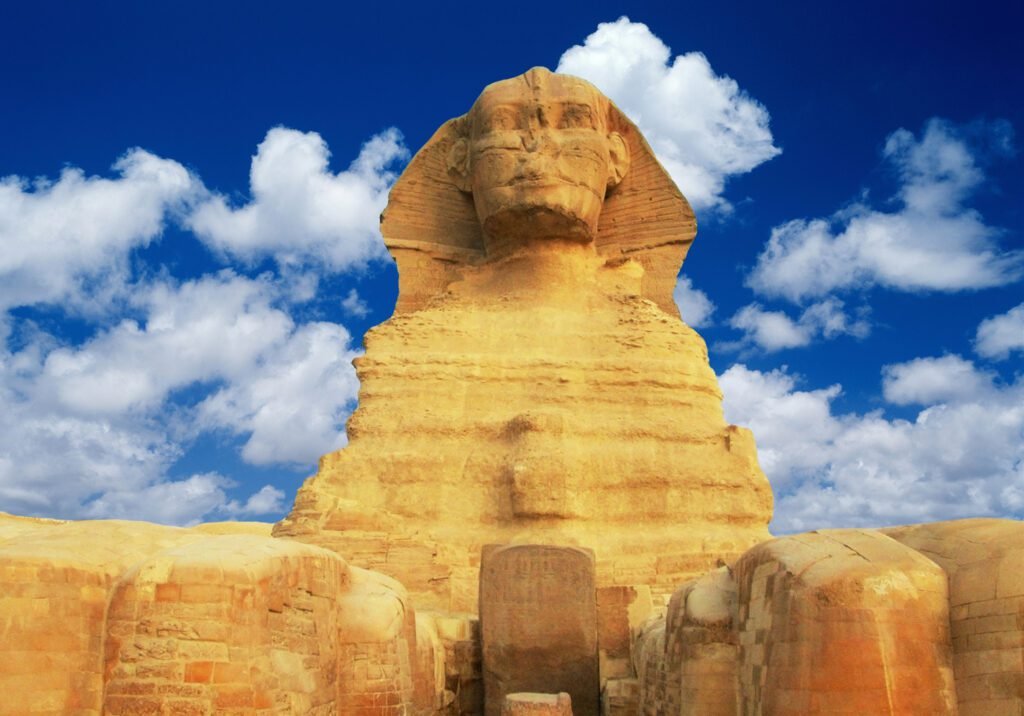

A sphinx (or sphynx) is a creature with a lion’s body and a human’s head, with minor variants. It is a well-known character in Egyptian, Asian, and Greek mythology.
Ancient Chinese Civilization (2100 BCE – 221 BCE)
The civilization of ancient China is one of the important civilizations that flourished and has a long-lasting impact. China has a rich history of thousands of years. Early Chinese Civilization was a place of great achievements in the field of culture, administration, art, and creativity. The great dynasties that ruled over China were mighty in power and had deep philosophical ideologies which formed a rich Chinese civilization.
Ancient China was ruled by several powerful dynasties. China has seen the rise and fall of many dynasties in its history. Each dynasty has its impact and impression on Chinese history. The oldest dynasties were the Xia Dynasty and Shang Dynasty, which created a centralized administration framework and had advanced bronze-casting skills. Later came the dynasties like Zhou, Qin, Han, Tang, and Ming, enjoying a time of tremendous amount of wealth, expansion, and cultural success.
Ancient China had detailed philosophical systems that influenced its culture and civilizations well beyond its borders. Confucianism, with its focus on ethics, family values, and harmony in society, plays a major role in Chinese administration and ethics. Taoism gave spiritual and philosophical guidance by emphasizing harmony with nature and embracing simplicity. Other schools of thought, such as Legalism and Mohism, also contributed to the philosophical base of ancient China.
The Great Wall of China is a tribute to ancient China’s amazing architectural achievements. This massive fortification, which covered thousands of kilometers and was built across multiple dynasties, served as a symbol of defense and togetherness. The vastness and perfection of ancient Chinese architecture may be seen in imperial palaces such as the Forbidden City of Beijing and awesome mausoleums such as the Terracotta Army of Qin Shi Huang.
The ancient Chinese were well-known for their contributions to science, technology, and creativity. Papermaking, printing, the compass, gunpowder, and early seismographs were examples of their pioneering mentality. Agricultural practice improvements, such as the introduction of new crops and sophisticated irrigation systems, permitted continued food production and population increase.
China’s cultural and literary legacy is vast. Traditional Chinese painting is a respected creative culture, with a focus on harmony, balance, and showing the spirit of nature. The Chinese writing system, with its complicated characters, aided in the production of timeless literary works such as “The Art of War” by Sun Tzu as well the poetry of Li Bai and Du Fu. In addition, ancient China’s traditional performing arts, music, and precise labor are still valued today.
The rich history, dynastic rule, philosophical ideas, and cultural achievements of ancient China influenced not just its own culture but also had a significant impact on the worldwide landscape. Ancient China’s legacy lives on in current Chinese culture and beyond, from its spectacular architectural accomplishments to its enduring literary and philosophical contributions. The impact of ancient China continues to inspire, enthrall, and enhance our knowledge of this great civilization’s achievements and lasting spirit.
Ancient Greece (800 BCE – 146 BCE)
The Ancient Greek Civilization is referred to as the first Western Civilization. Greek Civilization has a special place in history because of its contribution to philosophy, politics, art, and science. The civilization existed from the 8th Century B.C. to the 4th Century B.C. and it laid a strong foundation for the development of democracy, intellectual ideas, and art that are relevant to the modern world as well.
The development of democratic ideas in the city-state of Athens during ancient Greece is recognized. In the fifth century BCE, Athens pioneered the idea of direct democracy, in which people engaged directly in the decision-making process. To promote civic responsibility and individual rights and liberties, this type of government placed a strong emphasis on the equal involvement of all individuals.
Some of history’s best thinkers, whose contributions to intellectual thinking were deep, came from ancient Greece. Fundamental issues relating to life, ethics, politics, and the nature of knowledge were examined by Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. Their theories served as the foundation for critical analysis, logical reasoning, and the quest for knowledge, which have shaped Western thought for centuries.
The Olympic Games were created by the Ancient Greeks and are now a well-known custom in memory of the gods. Every four years, these athletic contests brought city-states together for friendly competition and promoted unity. In addition to showcasing participants’ physical strength and disciplined training, the games were followed by cultural festivals that featured poetry, music, and theatre.
Elegant, harmonious, and precise mathematics are the distinctive features of classical Greek architecture. Iconic constructions like the Parthenon on the Acropolis of Athens are clear examples of the ancient orders, which also include the Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian styles. The Greeks were experts in representing the human figure in sculpture, ceramics, and frescoes; examples include the Venus de Milo and the Discus Thrower (Discobolus).
Epics, dramas, and comedies from Greek literature are still praised for their universal themes and insightful depictions of human nature. Homer’s “Iliad” and “Odyssey” are considered epic classics, while playwrights like Sophocles, Euripides, and Aristophanes created tragedies and comedies that probed morality, fate, and societal difficulties in their tragedies and comedies. The theatrical arts and storytelling have been impacted by these works for a long time.
Greek philosophers contributed significantly to several scientific fields. Greek mathematicians set the groundwork for contemporary ideas in mathematics, from Pythagoras’ theorem through Euclid’s geometrical laws. Hippocrates and other academics contributed to the advancement of medicine with their methodical observations and empirical approach.
The achievements of the ancient Greeks serve as a model for modern society. Ancient Greece made an unforgettable mark on human history via the development of democracy, the basis of Western philosophy, creative excellence, and scientific research. Its legacy is still felt today in our governmental structures, moral principles, creative expression, and academic endeavors. Ancient Greece’s teachings and contributions are still evidence of its outstanding civilization’s lasting influence.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed about the main 5 Ancient and Earliest Civilizations of the World. The civilization of Mesopotamia, Indus Valley civilization, Ancient Egyptian civilization, Ancient Chinese civilization, and Ancient Civilization of Greece. These all have made major contribution to cultural growth, scientific growth, philosophy, and many other fields.
The world we are living in today is shaped by the ideologies of these great civilizations. The human community grew from nomads and reach the way we are living today, these civilizations were a milestone in Human Growth.
What are your thoughts, please comment.
Follow us on social media